RPI Best Practice Standards® Program Purpose
We believe that employee performance is the key to success for any organization. We know, based on extensive research, that employee performance is enhanced by systematic employee recognition, which is defined as
the acknowledgement of individual and team behavior that supports an organization’s goals and values.
The purposes of the RPI Best Practice Standards® program are to:
- Establish objective standards for evaluating employee recognition programs;
- Recognize organizations that successfully implement recognition programs; and,
- Provide illustrations of recognition RPI Best Practice Standards® with RPI’s membership.

STANDARD 1: Recognition Strategy
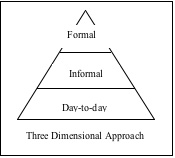
The organization has a written recognition strategy that articulates the philosophy and objectives for all recognition practices, including day-to-day, informal, and formal recognition programs. The recognition strategy provides purpose and direction
for how employee recognition encourages and rewards specific employee behaviors that advance the organization’s goals and objectives. All recognition activities are aligned with the mission and culture of the organization.
Day-to-Day Recognition encompasses a wide range of recognition practices that are frequent (daily or weekly), low or no-cost, often intangible, and often reliant on interpersonal skills for positive feedback that can be given to all employees
at all levels. Day-to-day recognition programs help peers and managers communicate expressions of appreciation and may include thank you notes, certificates that employees give to one another, or verbal praise. All employees (approximately 80
– 100 percent) participate in this level of recognition, supporting recognition throughout the organization.
Informal Recognition focuses primarily on performance achievements, goal accomplishments, and other milestones by individuals or teams that may occur monthly or quarterly and impact fewer employees than Day-to-Day recognition (approximately
30% to 50%). It is less structured than formal recognition and may include low-cost awards, refreshments, point-value incentives, gift cards, and certificates. Informal recognition programs may be utilized by peers and managers, with incentives
from peers to peers requiring management approval.
Formal Recognition consists of structured recognition programs with clearly defined objectives, processes, and criteria linked to rewarding and recognizing individuals, teams, or departments on a company-wide level for achieving specific
business targets, exemplifying specific organizational values, or performing actions that go above and beyond normal work expectations. Formal recognition also includes career milestones or service awards. Formal recognition often involves a nomination
and selection process and an awards ceremony where employees receive public recognition and are presented with awards in a formal setting. Most formal recognition programs occur less frequently (usually annually), involve more costly awards, and
recognize a smaller percentage of employees (approximately 1% to 10%).
A successful program includes intangible recognition (verbal and/or written praise in acknowledgement of individual or team achievement), awards (cash or tangible items for individual or team achievement), and celebrations (planned or spontaneous
events in recognition of individual or team achievement). Intangible recognition may involve a certificate or other token of appreciation. Celebrations may consist of an informal team lunch or an organization-wide event. Successful recognition
programs use a variety of motivational tools and communication methods to maximize opportunities to positively reinforce behavior that is consistent with the organization’s goals and values.
Back to Standards List

STANDARD 2: Management Responsibility
Senior leaders and management actively endorse and are held accountable for planning, supporting, reviewing and actively participating in the recognition programs.
Recognition Strategy
Senior leaders participate in defining the recognition strategy and objectives and hold recognition professionals and other managers accountable for implementing them and achieving stated goals.
Recognition Policy & Procedures
Senior leaders approve the recognition policies, procedures, and documentation required to implement, maintain, review, and improve all recognition programs.
Recognition Program Administration
Senior leaders ensure that qualified individual(s) are assigned to manage all recognition programs and approve the selection of support staff, such as administrative teams and committee members. Senior leaders also ensure that appropriate reporting
structures are established for regular reviews.
Empowerment of Program Administrators
Senior leaders delegate sufficient authority so that those responsible for the recognition programs are able to contribute their expertise in developing a recognition strategy; ensure that all recognition programs are consistent with the organization’s
strategy and goals; negotiate with vendors for award options; create and administer recognition budgets; schedule, plan, and facilitate events and celebrations; and develop measures to evaluate program effectiveness.
Support and Involvement
Senior leaders actively support recognition practices and participate in using them.
Resources
Senior leaders provide adequate resources to encourage and reinforce exemplary recognition practices.
Back to Standards List

STANDARD 3: Recognition Program Measurement
The organization evaluates the effectiveness of its formal and informal programs using measures that are statistically reliable and valid and substantive in nature. Ideally, the organization should have data that evaluate how well its programs are
implemented and their impact on attitudes and productivity. Historical data that demonstrate effectiveness should be presented for a minimum period of at least one year.
Implementation
The organization measures how well its programs are implemented, including training, communication, and the presentation of awards. Examples could include percent of supervisors trained, nominations per employee or per dollar spent, number of times
a website was accessed, number of spot awards distributed, and number of individuals recognized in department meetings.
Participation
The organization documents the level of employee participation in all parts of the recognition strategy, including specific programs. Examples could include number of nominations submitted, number of citations per employee, number of visits to a website,
or number of employees attending a recognition event.
Employee Satisfaction
The organization demonstrates improvements in employee satisfaction as a result of the recognition programs, and explains how employee satisfaction is measured. Examples could include changes in measures of employee satisfaction, employee surveys,
focus groups, and employee engagement.
Productivity
The organization measures how its programs improve productivity and organizational effectiveness. Examples could include changes in absenteeism, turnover, productivity, profitability, or other organizational metrics.
Back to Standards List
 STANDARD 4: Recognition Program Communication Plan
STANDARD 4: Recognition Program Communication Plan
The organization establishes and maintains a strategic communication plan that communicates all aspects of the recognition strategy, including program objectives, recognition processes, events, celebrations, tools, and a contact person for program
information.
Communication Plan
The communication plan should describe the processes that have been created to inform all employees how the recognition programs operate, how they can participate in them, and who is being recognized and why. The organization has specific communication
goals that are periodically measured for effectiveness. Communication goals are easily understood by all, compelling, and action-oriented.
Communication Tools
The organization may use several initiatives and tools for communicating messages to various audiences, including electronic technologies that can effectively reach targeted audiences. Examples may include bulletin boards, posters, videos, intranet,
internet, email, letters, manager tool kits, and employee handbooks. The communication tools will vary according to an organization’s scope and size.
Back to Standards List
 STANDARD 5: Recognition Training
STANDARD 5: Recognition Training
Training is essential in creating a culture of appreciation; all employees, especially managers and executives, need to understand the importance of meaningful recognition and how to give it. The organization documents how training is designed and
administered for managers and employees at all levels, including the training objectives, methods, and curriculum.
Training Emphasis
The organization demonstrates that training is an important element in its overall recognition strategy by devoting the necessary time and resources to it. Training should be structured in the manner that best fits an organization’s structure and
culture. Elements of a successful training strategy may include individual learning, web-based learning modules, e-learning, train-the-trainer instruction, manager tool kits, printed materials, video presentations on how to reward and recognize
others, and new-employee orientation training.
Training Results
The organization demonstrates that the recognition training has achieved desirable results. The results describe how the training helps employees and managers develop skills and learn how to use the recognition programs.
Back to Standards List
 STANDARD 6: Recognition Events and Celebrations
STANDARD 6: Recognition Events and Celebrations
The organization demonstrates how celebrations and award ceremonies are effectively used to recognize its employees. Creativity and uniqueness are used to provide meaningful experiences that make employees feel appreciated and the results are tracked
to provide continuous improvement.
Responsibility
The organization assigns responsibility for planning meaningful events and celebrations. These people demonstrate creativity in their planning so that those who are recognized feel individually acknowledged.
Resources
The organization devotes adequate resources (funding and staff) to the planning and execution of periodic celebrations and special events. The organization allocates resources to track the results of events.
History and Documentation
The organization demonstrates how photos, videos, and other media are used to document the events and celebrations and to enhance the overall recognition program by providing communication to relevant audiences after the events. Historical data should
be kept regarding the number of invitees, number of attendees, cost per person, and other data to show the success of event.
Back to Standards List
 STANDARD 7: Program Change and Flexibility
STANDARD 7: Program Change and Flexibility
The organization encourages flexibility in its recognition program. As changes arise, the organization demonstrates its ability to adjust to changing goals and objectives and the diverse recognition needs of its employees through feedback and employee
survey programs. Programs are consistently reviewed for possible changes, modifications, and restructuring.
Change Management
The organization describes how changes to the recognition program are implemented. This may include:
- Adjusting the recognition program to reflect changing organizational goals.
- Tailoring recognition to meet the diverse needs of individuals and teams throughout the organization.
Management Review
Senior leaders regularly review recognition programs to ensure alignment with business goals and organization values. Managers are held accountable for overall recognition effectiveness in achieving business objectives, evaluating recognition program
metrics, and providing opportunities for innovation and improvement.
Continuous Process Improvement
Accountability, review, and continuous improvement processes are practiced on a regular basis to advance the quality and effectiveness of all recognition programs and to ensure that each employee receives a consistent, authentic, and meaningful recognition
experience when such recognition is given.
Back to Standards List